dq.plot.wigner
wigner(
state: QArrayLike,
*,
ax: Axes | None = None,
xmax: float = 5.0,
ymax: float | None = None,
vmax: float = 2 / jnp.pi,
npixels: int = 101,
cmap: str = "dq",
interpolation: str = "bilinear",
colorbar: bool = True,
cross: bool = False,
clear: bool = False
)
Plot the Wigner function of a state.
Warning
Documentation redaction in progress.
Note
Choose a diverging colormap cmap for better results.
Warning
The axis scaling is chosen so that a coherent state \(\ket{\alpha}\) lies at the
coordinates \((x,y)=(\mathrm{Re}(\alpha),\mathrm{Im}(\alpha))\), which is
different from the default behaviour of qutip.plot_wigner().
See also
dq.wigner(): compute the Wigner distribution of a ket or density matrix.dq.plot.wigner_data(): plot a pre-computed Wigner function.
Examples:
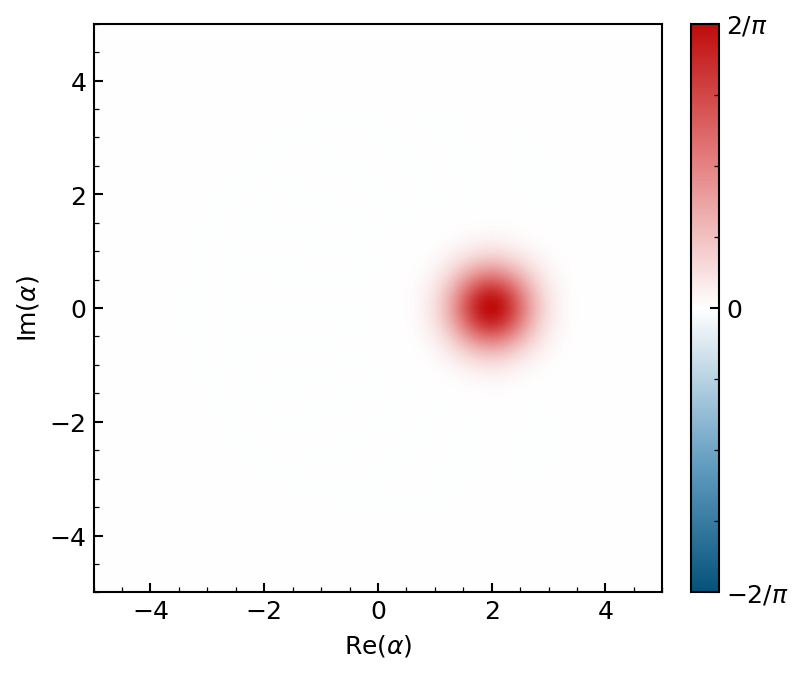
>>> psi = dq.coherent(16, 2.0)
>>> dq.plot.wigner(psi)
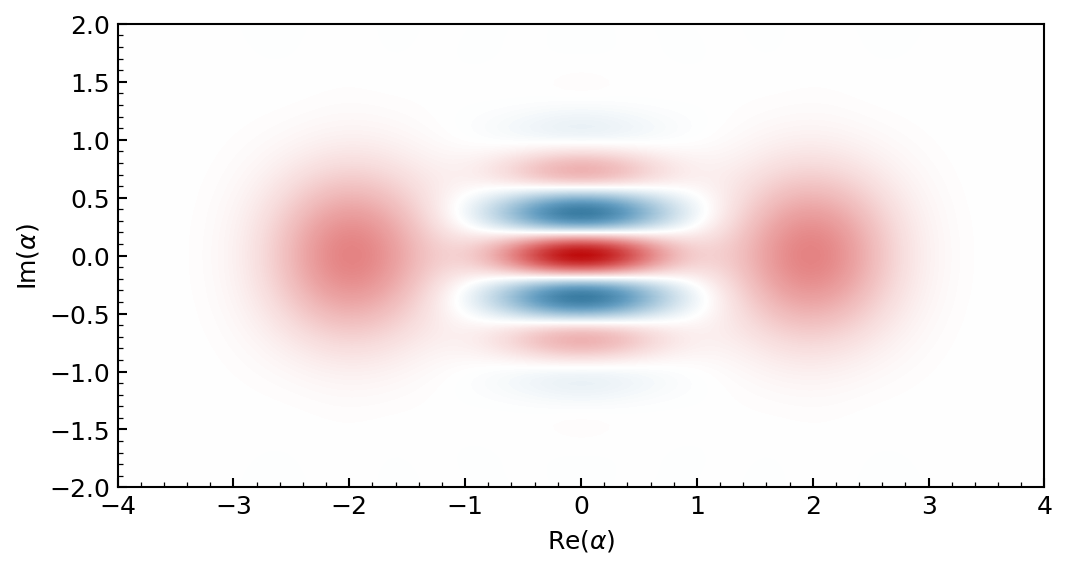
>>> psi = (dq.coherent(16, 2) + dq.coherent(16, -2)).unit()
>>> dq.plot.wigner(psi, xmax=4.0, ymax=2.0, colorbar=False)
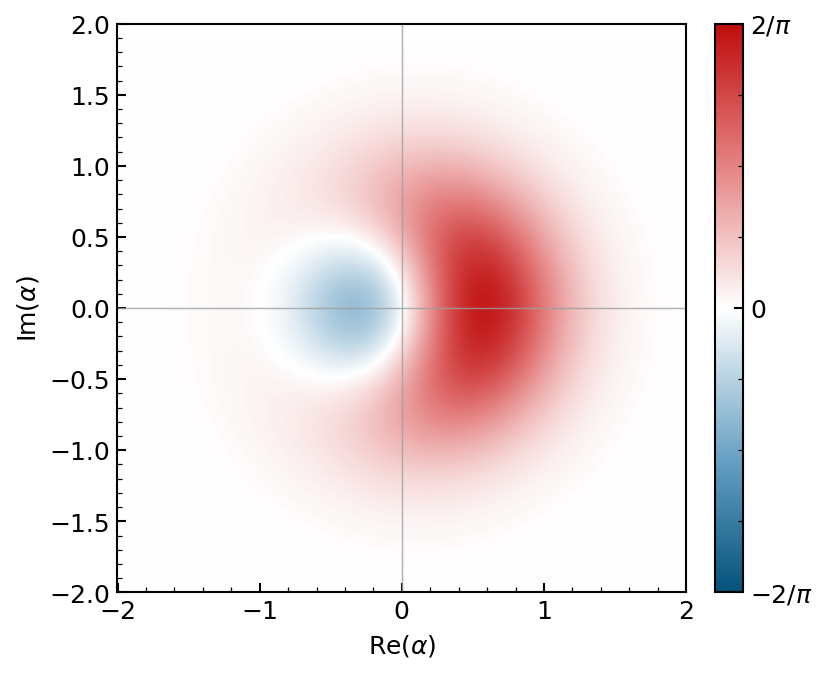
>>> psi = (dq.fock(2, 0) + dq.fock(2, 1)).unit()
>>> dq.plot.wigner(psi, xmax=2.0, cross=True)
>>> psi = dq.coherent(32, [3, 3j, -3, -3j]).sum(0).unit()
>>> dq.plot.wigner(psi, npixels=201, clear=True)